The Concept of the Disease
Burkitt lymphoma is a highly aggressive tumour of germinal centre B-cells defined by phenotype and the presence of a MYC rearrangement.
How is it Diagnosed?
Tissue Biopsy or Bone Marrow
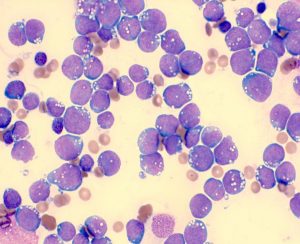
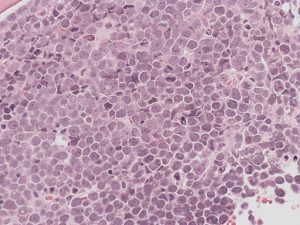
- Highly proliferative large lymphoid cells replacing normal tissue architecture
- An aberrant germinal centre B-cell phenotype detected by flow cytometry or immunocytochemistry, including absence of BCL2 protein expression
- The presence of a balanced translocation involving MYC and immunoglobulin heavy or light chain genes detected by FISH
Tissue Biopsy Imprint Morphology
Tissue Biopsy Morphology
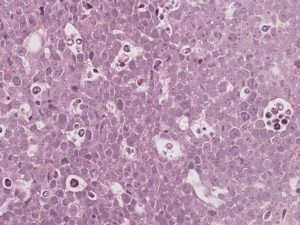
Immunocytochemistry
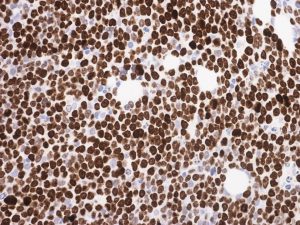
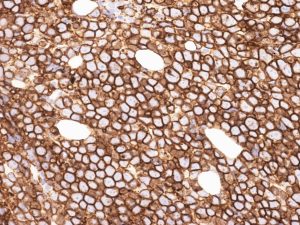
FISH
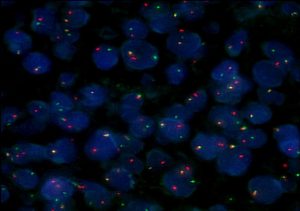
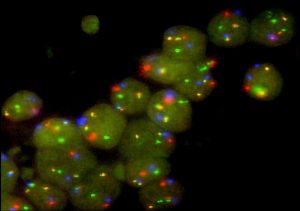
What is the Clinical Outcome?
BL is a highly aggressive malignancy and is rapidly progressive in most cases. R-CHOP chemotherapy used to treat DLBCL is not effective. In contrast about 60% of those treated with R-CODOX/M-IVAC are cured and the incidence of post treatment relapse is low. However, in contrast to R-CHOP this treatment has significant morbidity and mortality and accurate diagnosis is essential.
Age and overall fitness at presentation are the major prognostic factors.

