The Concept of the Disease
In normal lymphoid tissues, germinal centres are formed by B-cells responding to antigenic stimuli. Through rapid cellular proliferation, with mutation and rearrangement of immunoglobulin genes, the population of B-cells that can respond to the antigen is expanded and the affinity of the antibodies increases. This is a pivotal step in the normal immune response.
Follicular lymphoma is a tumour of germinal centre cells. The tumour cells share many of the features of B-cells in the normal germinal centre.
How is it Diagnosed?
Lymph Node Biopsy
- Cells with the morphology of germinal centre cells forming structurally abnormal B-cell follicles and spreading into spaces normally occupied by other cell types
- Identification of an abnormal germinal centre phenotype by immunocytochemistry or flow cytometry; most importantly, demonstration of abnormal expression of the anti-apoptotic protein BCL2
- Demonstration of B-cell monoclonality
- Demonstration of a t(14;18) translocation which deregulates expression of the BCL2 gene
Lymph Node Morphology
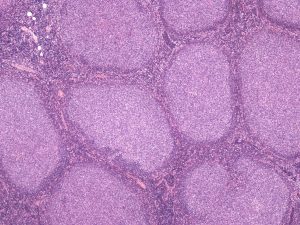
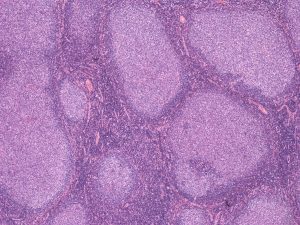
Bone Marrow
- The bone marrow is frequently involved in follicular lymphoma
- Tumour cells tend to aggregate close to bone
Bone Marrow Trephine Morphology
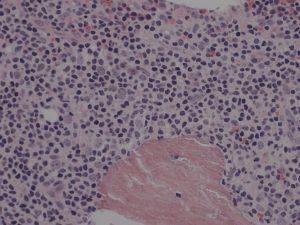
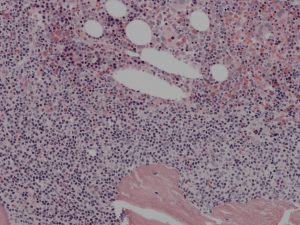
What is the Clinical Outcome?
The clinical outcome is highly variable; treatment is given primarily on the basis of symptoms and 75% of patients will survive for more than 5 years.
- Many patients require no immediate treatment or receive local radiotherapy only.
- Most symptomatic patients have a prolonged period of remission when treated with R-CVP or R-CHOP.
- A minority of patients have progressive or rapidly relapsing disease. In some cases the tumour undergoes a qualitative change with transformation to diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
The standard assessment of prognosis is the follicular lymphoma international prognostic index (FLIPI).
| Score | FLIPI Risk Group |
| 0 – 1 | Low |
| 2 | Intermediate |
| ≥3 | High |
| Risk Factor | Score +0 | Score +1 |
| Age (years) | ≤60 | >60 |
| Stage (Ann Arbor) | I or II | II or IV |
| Number of extranodal sites | 0 or 1 | >1 |
| Performance Status (ECOG) | 0 or 1 | >1 |
| Serum LDH | Normal | Raised |

